🚩Red Flags – Common Scam Warning Signs
How and when do you decide you should stay away from that text, email or any suspicious communication received
- Creates a sense of urgency and call for immediate action with a date or hours left to respond, words like “Click now”, “Expires in 4 hours” etc.
- Unfamiliar sender or other recipients.
- Spelling and grammatical errors.
- Deliberate obfuscation of spelling example using zero instead of the letter ‘O’ and other such trick substitutes of the actual letters or joining of two words together by removing the space in between.
- Lack of personalisation and generic greeting like just “Hello”, “Hi” or “Hello Sir” etc.
- Threatening of negative or punitive action like electricity/phone would be cut, money will not be accessible, account will be blocked, losses need to be made good, or blackmail for something purportedly illegal etc.
- Attractive promises that are too good to be true with hope of huge returns or rewards, such as winning a lottery you never participated in, quick large returns, or far cheaper than average goods.
- Mismatch – sender’s email domain and organisation name don’t line up, phone belongs to a different region than the organization etc. Sender’s email is a generic email such as Gmail or Hotmail when the sender claims to be from a government department.
- Clumsy design work, poor content and functionality of website that looks sketchy or hurriedly done, logos look weird or of poor quality images.
- Social Media profile has few connections, if any and not too many details filled out.
- Unfamiliar tone – For example your boss is sounding extra formal or a friend you haven’t met in years is sounding over familiar.
- Suspicious attachments or links embedded in the message and you are being asked to click on a link or download a file, especially one that is macro enabled indicates a possible scam.
- Link you have received points to a site which looks like your bank or other familiar site but still different and starts with only http:// as against https:// (https:// denotes that it is a secure website).
- Request for payment or personal credentials – Forms and requests to fill out personal or sensitive information or payment details – like credit card number, ATM / Credit card PIN, Aadhar card number, OTP etc.
- Short and ambiguous – Scammers sometimes keep details limited in the hope of getting lucky. So you may see messages like “Here’s what you requested” without the details.
- You did not initiate the conversation or the sender is unexpected – For example you get a response from HR on a job you did not apply for, or from a courier company for a package you did not order.
- Misleading links and short url links and non-secure websites that start with just http and no padlock – Hover your mouse cursor over links in emails. When your mouse cursor hovers over a link, a small window will appear above the link to show you the actual URL, which is the real destination of the link. If the links are mismatched, it is a strong indicator that something ‘phishy’ is going on. If you are using a mobile device, long-press the link to display a window with the actual URL. Be careful not to tap and open the link!
- Unusual and non-traditional payment mechanism being asked for; for example gift cards, cryptocurrency or other such tender that is hard to trace.
- Top line search items returned and paid Ads – sometimes scammers mimic good brands and place fake ads to get on top of the search results.
- Image only emails. Or Emails where the return address on the email header is different than the one that seemingly sent the email.
Cybersecurity Best Practices – Do’s and Don’ts
Published by I4C and the Ministry of Home Affairs
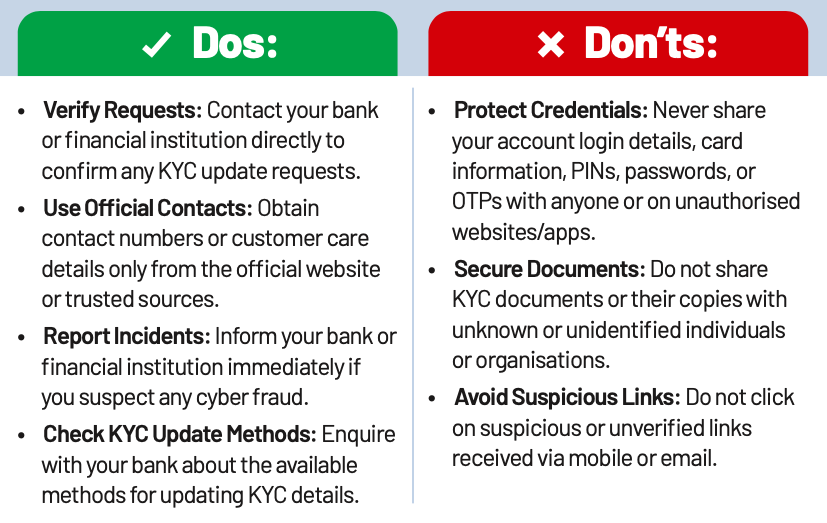
KYC Scam
KYC Fraud involves cybercriminals exploiting identity verification processes to steal personal information, commit identity theft, or access financial accounts illegally. This can lead to significant financial losses and reputational damage for individuals, businesses, and financial institutions. Common tactics include tricking people, forging documents, and creating fake identities.
Online Job Scam
Online Job Scams trick people looking for work. Scammers post fake jobs on websites, social media, or send emails, offering high pay and easy work. Their goal is to steal the victim’s money or personal information.

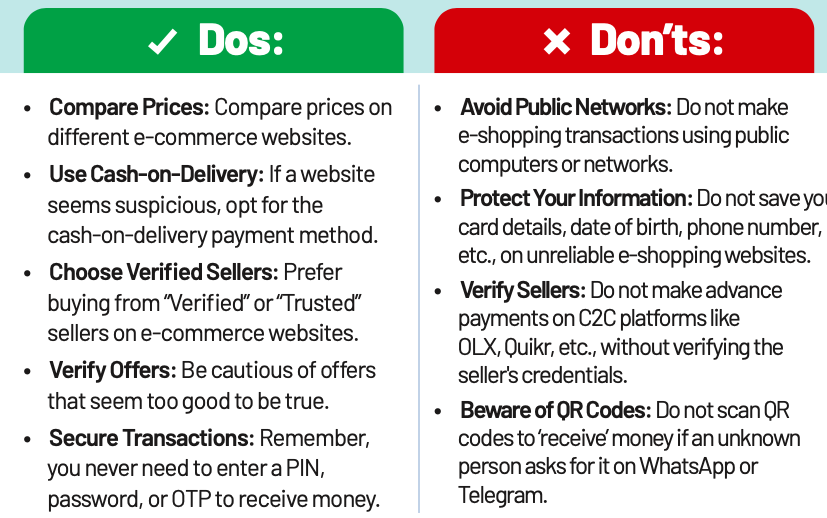
Online Shopping Fraud
Online Shopping Fraud is a cybercrime where fraudsters deceive victims into making illegitimate purchases. They create fake websites or manipulate legitimate platforms, offer deals that are too good to be true, and steal personal and financial information, leading to financial losses and mistrust in online marketplaces.
Digital Arrest
Digital Arrest is when someone is detained or restricted through digital means (like video calls) instead of traditional physical arrest methods. This often involves scammers impersonating government officials to extort money.

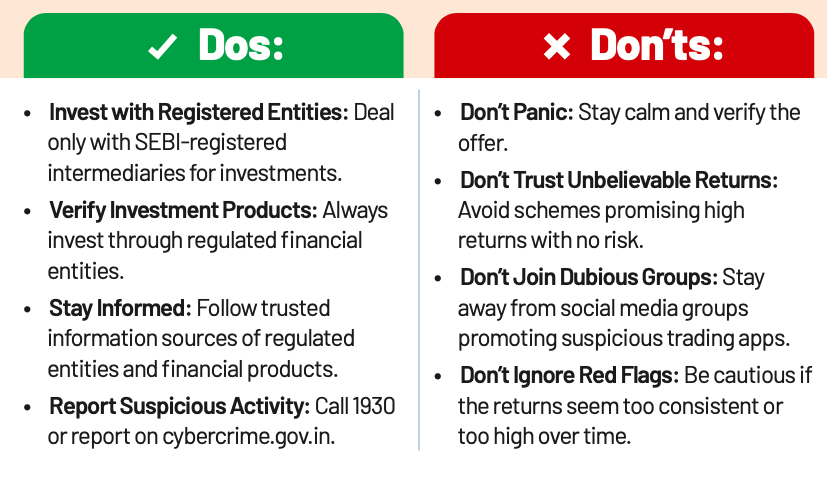
Investment Scam
An Investment Scam involves fraudulent schemes that promise high returns, often too good to be true. These scams pay earlier investors with the money of new investors instead of generating profits through legitimate economic activity. It is also known as Ponzi scheme.
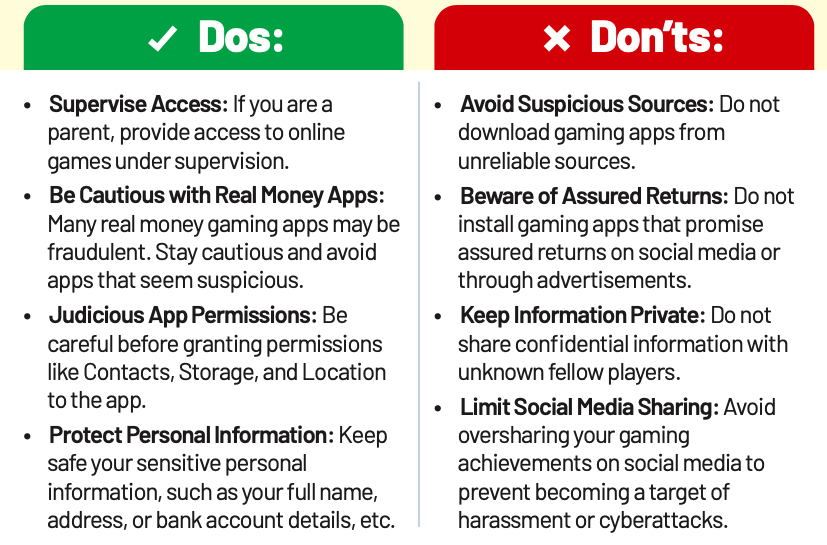
Online Gaming
Online Gaming has become a hotspot for cybercriminals, with threats ranging from virtual theft and account breaches to real-world financial fraud and identity theft. Attackers exploit platform shortcomings and target players through phishing scams, malware, and social engineering.
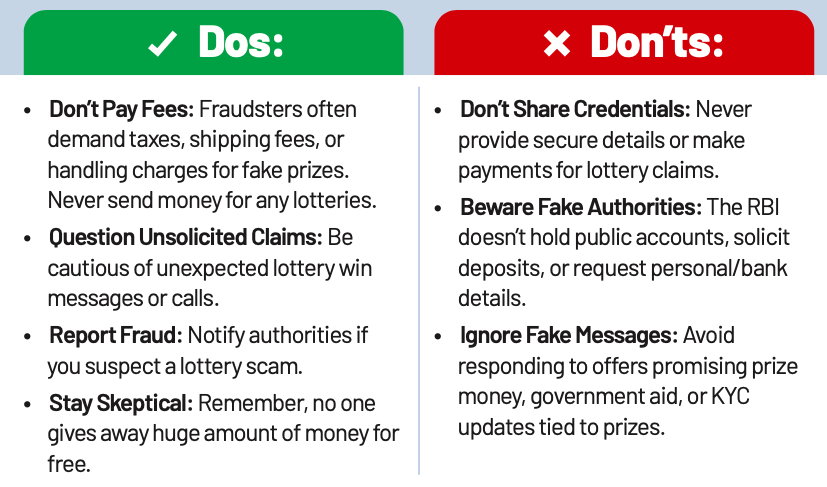
Lottery Fraud
Lottery Fraud scams deceive people into believing they’ve won a prize to trick them into sending money or sharing personal information. These schemes exploit the hope of financial gain but are always too good to be true.
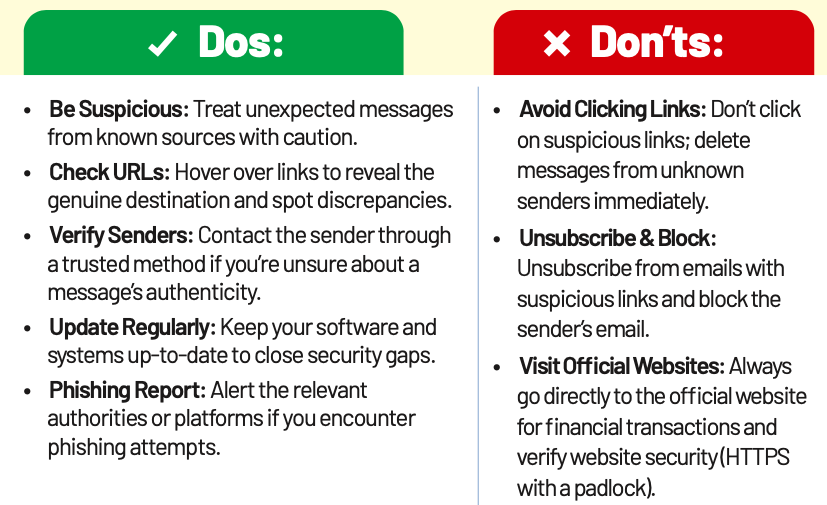
Phishing
Phishing is a common cybercrime tactic that deceives victims into clicking on fake links. These links appear as emails or websites from trusted sources but redirect users to fraudulent sites designed to steal sensitive data, such as login credentials, personal information, or financial details. Phishing can also install malware, giving cybercriminals unauthorised access to your device.
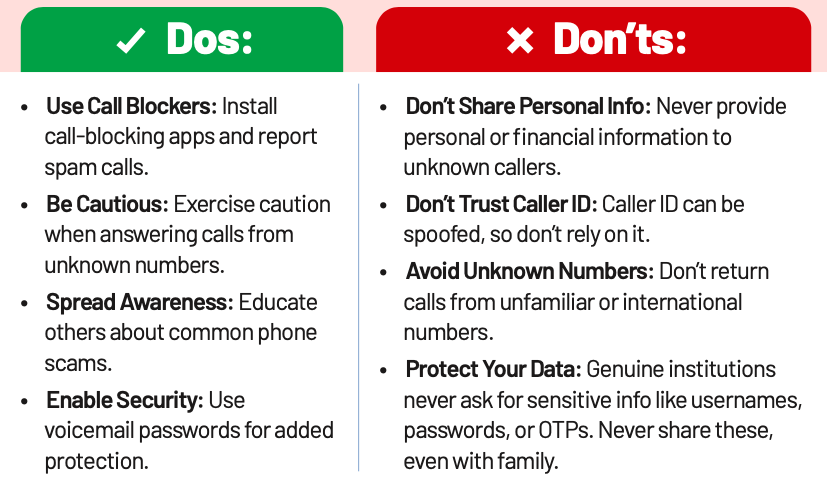
Spam/ Vishing Calls
Spam/Vishing Calls (voice phishing) are a deceptive form of cybercrime. Fraudsters use social engineering to trick victims into revealing sensitive information, like personal or financial data. They often impersonate legitimate entities, such as banks or government agencies, using tactics like caller ID spoofing and urgency to gain trust and steal information.
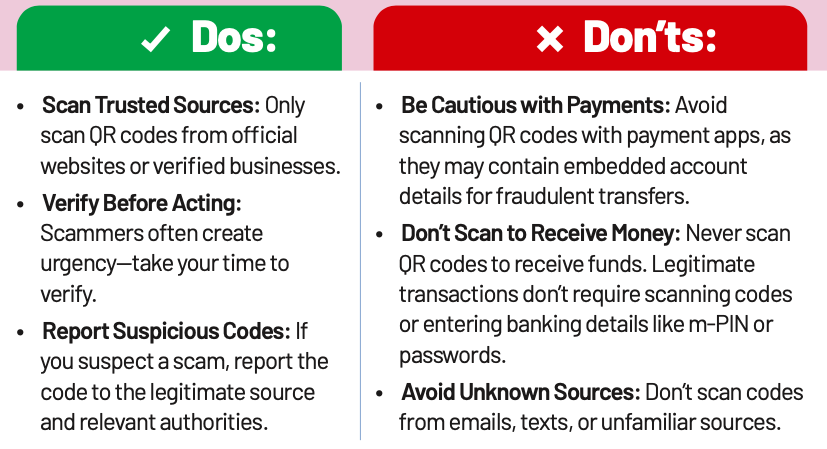
Quishing
Quishing Scams are on the rise. The scammer lures victims with promises of deals or convenience by asking to scan QR codes but ultimately initiate unauthorised financial transactions. Malicious codes can redirect users to phishing sites, steal login credentials, or transfer money directly to the scammer’s account.
Search Engine Fraud
Search Engine Fraud occurs when fraudsters manipulate search results to display fake contact information, posing as legitimate entities. Victims who unknowingly call these numbers may reveal sensitive information, such as passwords and account details, leading to financial loss, identity theft, and other severe consequences.

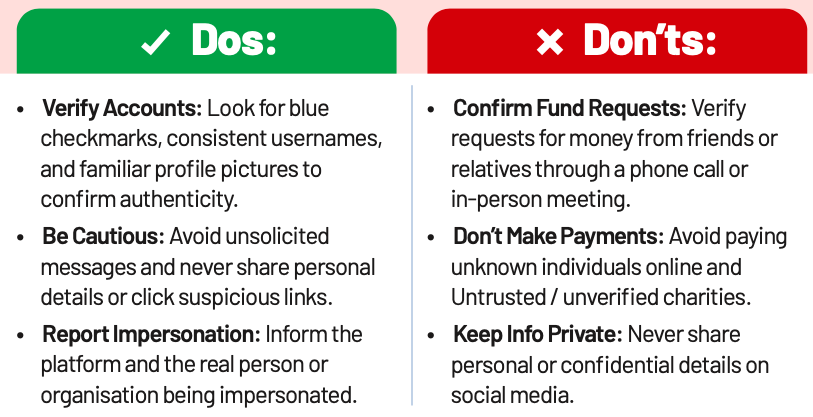
Social Media Impersonation
Social Media Impersonation happens when someone sets up a fake account mimicking a real person or organisation. These fraudulent accounts are used to deceive others, often leading to identity theft, financial scams, reputation damage, and the spread of false information.
SMS, Email and Call Scams
SMS, Email, and Call Scams are used by fraudsters to deceive victims with fake offers . They impersonate trusted NBFCs by using their logos and fake IDs, gaining credibility. Scammers may send counterfeit sanction letters or cheques, asking for upfront payments. Once the payment is made, the fraudsters disappear with the money.

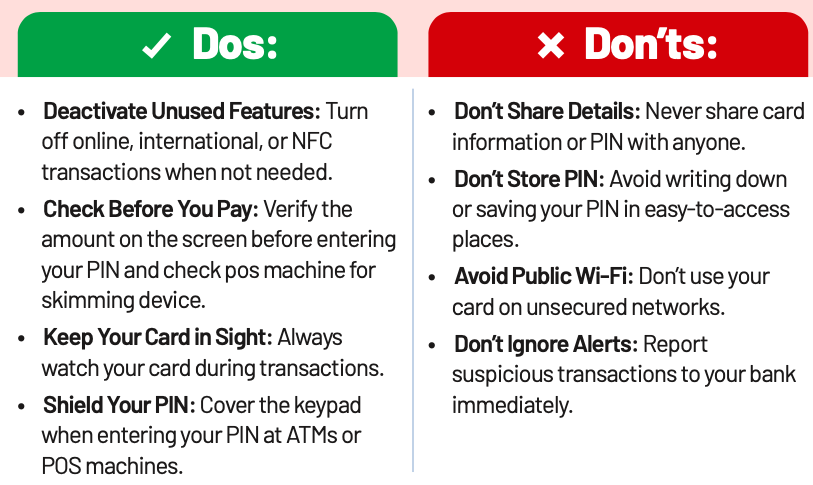
Debit/ Credit Card Fraud
Debit and Credit Card Fraud occurs when your card details are used without your consent for unauthorised transactions. Criminals may steal your physical card, skim your details, or trick you into sharing sensitive information through phishing scams.
Mobile Application APK Scam
Cybercriminals create Fake Mobile Banking Apps that closely resemble legitimate ones, using similar logos and interfaces. These apps are distributed through unofficial channels like third-party app stores or phishing links. Once installed, they steal your banking credentials and personal data, leading to financial fraud and identity theft.

Cyber Slavery
Cyber Slavery involves the exploitation of individuals through digital platforms, where they are coerced or manipulated into working without fair compensation. It overlaps with human trafficking and forced labour but specifically uses the internet and digital tools for exploitation.

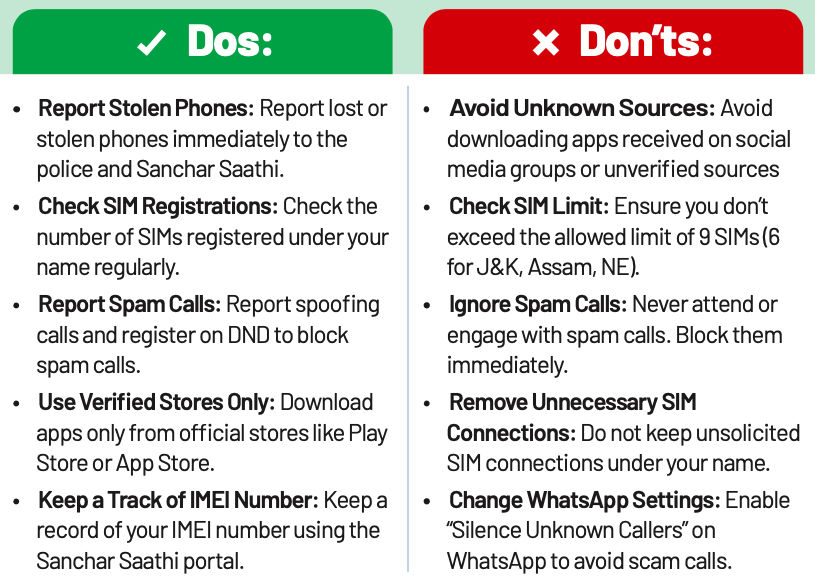
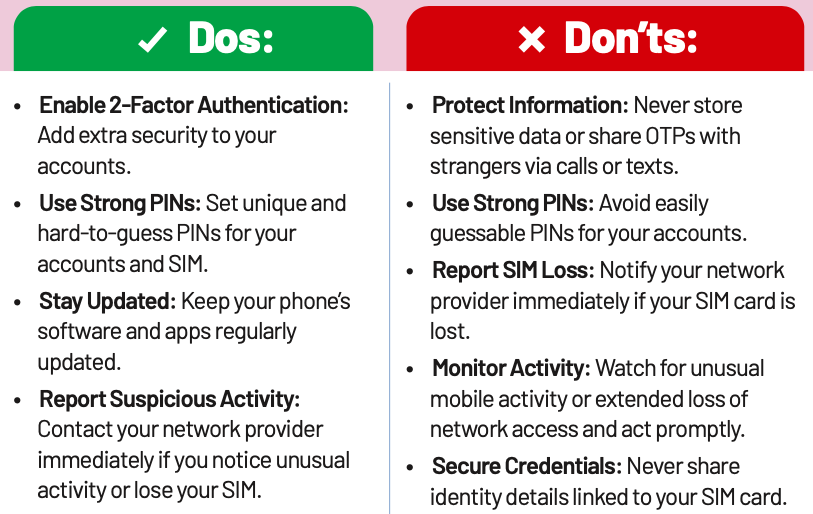
Sim Swapping
SIM Swapping is a cybercrime where fraudsters transfer your phone number to their SIM card. This gives them access to your calls, texts, and two-factor authentication codes, enabling identity theft, account hijacking, and financial fraud. Scammers often pose as network staff offering upgrades or benefits to trick you into revealing personal details.
Money Mules
Money Mules are individuals, knowingly or unknowingly, used to launder illegally obtained funds. Scammers persuade them to receive and transfer stolen money in exchange for commissions. These funds are moved across multiple accounts to obscure the fraudster’s identity. Involvement in such activities, whether intentional or not, is illegal and carries severe legal consequences.

Juice Jacking
Juice Jacking is a cybersecurity risk associated with compromised public USB charging stations. Hackers can exploit USB ports that charge and transfer data, using them to install malware or steal sensitive information. While no confirmed cases exist, staying vigilant is essential.

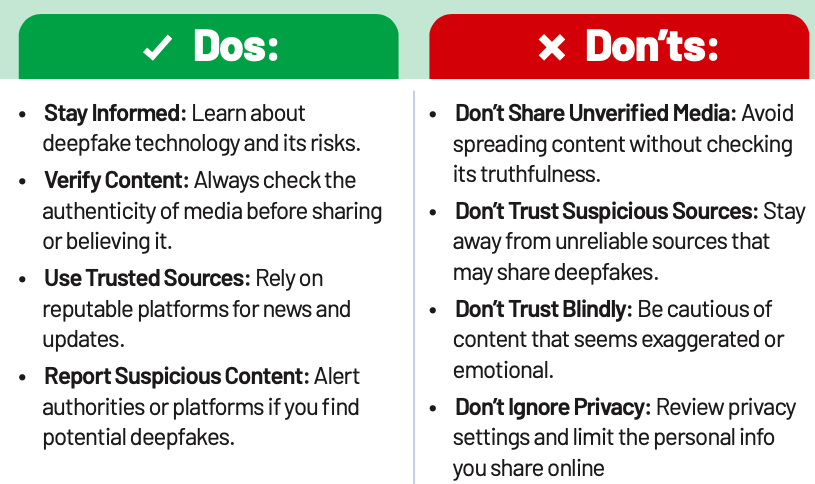
Deepfake Cybercrime
Cybercriminals use advanced AI to create fake videos or audio clips by manipulating real footage or recordings. These fake media are then spread through social media, messaging apps, and emails, often targeting public figures, celebrities, or people in authority. The goal is to deceive viewers, manipulate opinions, or spread false information. Criminals may use social engineering techniques to make the deepfake seem real, putting individuals and organisations at risk.
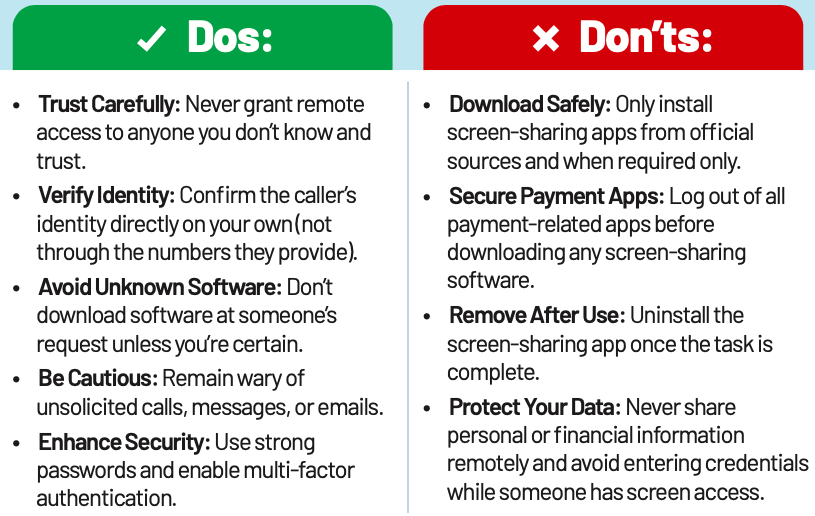
Remote Access Fraud
Remote Access Fraud occurs when cybercriminals impersonate trusted entities. They trick individuals into granting unauthorized access to their devices through screen-sharing apps. Once granted access, they can steal sensitive data, take control of accounts, and carry out fraudulent transactions.
Secure Browsing
Secure Browsing involves using practices and tools to protect yourself from online threats like phishing, malware, and identity theft while surfing the internet. It ensures safer interactions with websites and reduces cyber risks.

Ransomware
Ransomware is a type of malicious software that locks a victim’s files, making them inaccessible. Attackers then demand a ransom payment in exchange for key to unlock the file. Ransomware can spread through phishing emails, malicious software downloads, and security flaws. It poses a severe threat to individuals and organizations, causing significant data loss and financial damage.

Smartphone Scams
Mobile scams are on the rise, with fraudsters using fake calls, malicious apps, and SIM-related frauds to steal data and money. Scammers often disguise themselves as legitimate agencies to trick users into sharing personal details. Protect yourself by following these safety measures.